DUILIO F4
A motion control board that coordinates multiple motors and adds safety logic for machines.
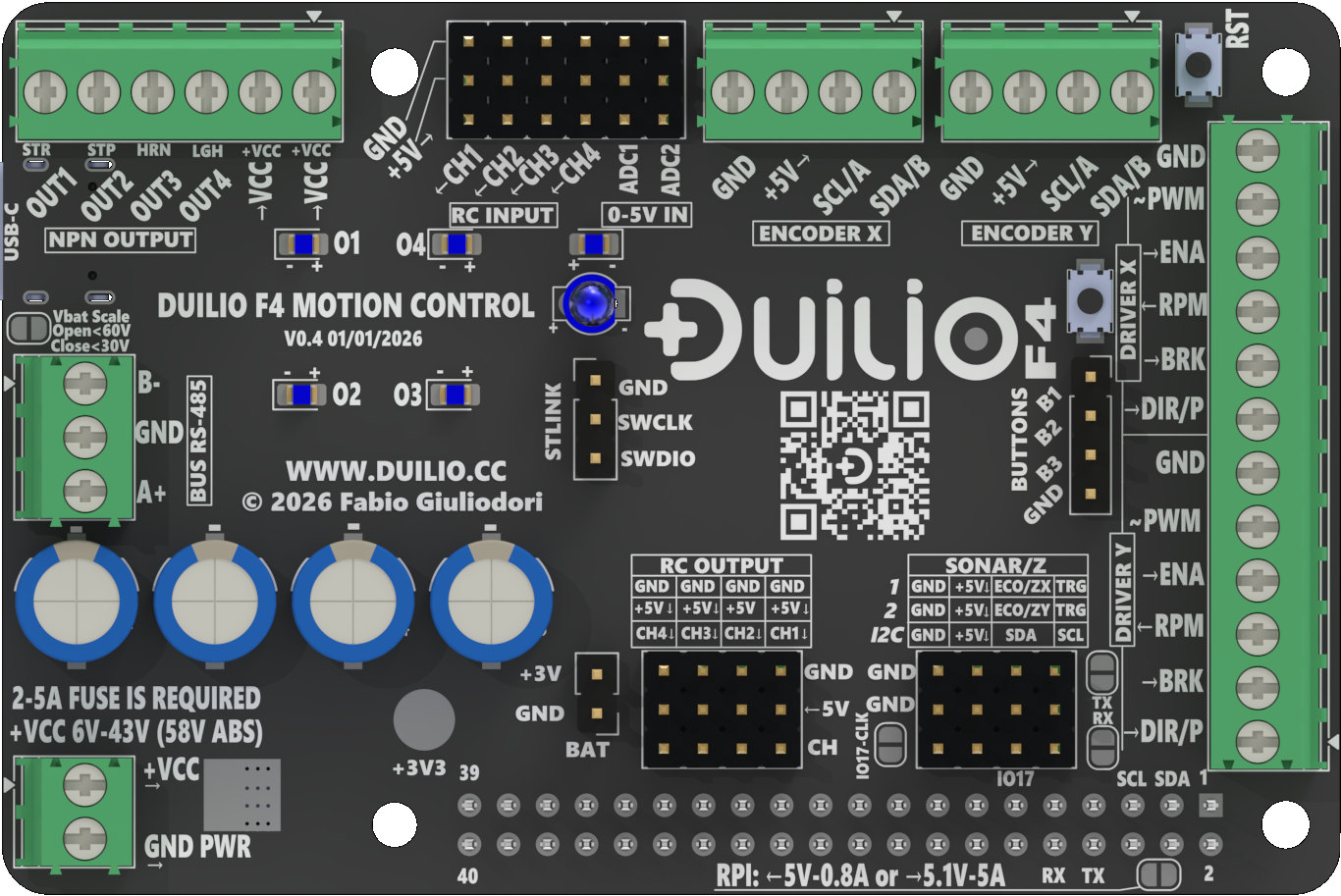
Three roles for machines, robots, and modular systems

Standalone motion controller
Run multi-axis motion with onboard coordination and safety.
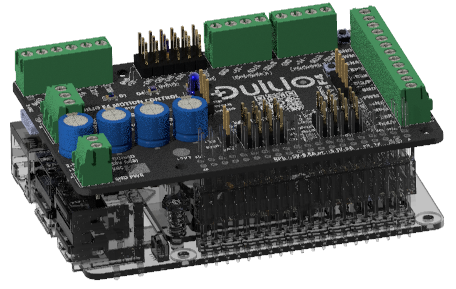
Raspberry Pi HAT / companion
Pair with a host computer for high-level control.

Bus expansion node
Extend distributed systems over RS485.
Key features
DUILIO F4 - Key features
This page provides a structured technical overview of DUILIO F4, covering STM32 motion control capabilities, safety and failsafe behavior, I/O, and supported motor driver interfaces for robotics and machines.
Project documentation is available on GitHub.
Motion control and safety
I/O and interfaces
System architecture
DUILIO F4 uses a distributed architecture with a clear split between host logic and real-time motion control. The host handles UI, networking, and coordination while Duilio nodes execute time-critical tasks. The system scales over RS485, allowing multiple Duilio boards on the same bus.
| Section | Details |
|---|---|
| MCU |
|
| Motion control |
|
| Scalability |
|
| Motor drivers |
|
| Encoders and feedback |
|
| RC I/O |
|
| Digital I/O (power) |
|
| Digital I/O (logic) |
|
| Analog inputs |
|
| Sensors |
|
| Safety and failsafe |
|
| Configuration |
|
| Host systems |
|
| Power |
|
| Raspberry Pi power output |
|
| Protection |
|
| System philosophy |
|
Motor driver compatibility
DUILIO F4 works with many external motor drivers. Compatibility depends on the control interface used by the motor driver, while DUILIO handles motion logic and coordination.
Supported control interfaces
- PWM + DIR (5 V)
- ENABLE + DIR + PWM (5 V)
- Dual PWM (forward / reverse)
- STEP / DIR (speed or position profiles)
- Analog speed (0-5 V)
- Analog speed + direction (0-5 V)
- RC-style PWM (ESC / servo)
Commonly used motor driver families
Examples for reference only, not official support:
- ZS-X11 series
- BLD-300 / BLD-510
- BTS7960 (IBT-2 modules)
- ODrive
- VESC
- Industrial and industrial-light drives such as Nanotec, Leadshine, Oriental Motor, Trinamic, Delta Electronics, Omron, SINAMICS, Maxon, Bosch Rexroth, Parker, Lexium, Panasonic
Specific compatibility depends on wiring and firmware profile. Some drivers are already used in real applications, others are under evaluation.
Comparison / Positioning
From Controllers to Motion-Control System Cores
Most controllers are designed to run code.
DUILIO F4 is designed to run machines.
This comparison highlights architectural differences, not raw performance.
| Controller | 5V logic compatibility | High-resolution analog inputs | Designed failsafe logic | Multi-motor coordination | Wide input voltage range | Can power peripherals (e.g. Raspberry Pi) | Works with external motor drivers | System watchdog & safety states | Time to a working motion system | Cost efficiency (typical) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino UNO / MKR | ||||||||||
| Arduino GIGA R1 | ||||||||||
| ESP32 | ||||||||||
| STM32 Nucleo | ||||||||||
| DUILIO F4 |
Note: Scores reflect typical system-level usage, not raw MCU capabilities. General-purpose boards may require extra hardware and firmware to reach similar safety and motion features.
Why it exists / Problem it solves
The story behind Duilio
Duilio was born as part of a larger remote-driving project.
The original goal was to let Fabry drive a real machine remotely, from his PC.
Building real machines quickly revealed the weak point: motors and drivers worked, but motion logic was fragile and never reusable.
Every controller meant rewriting ramps, limits, coordination and failsafe behavior.
So I designed a dedicated motion controller.
Not for demos, but for real machines -- safe, repeatable and scalable.
That controller is Duilio.
-- Fabio Giuliodori